Minoan eruption
Updated: Wikipedia source
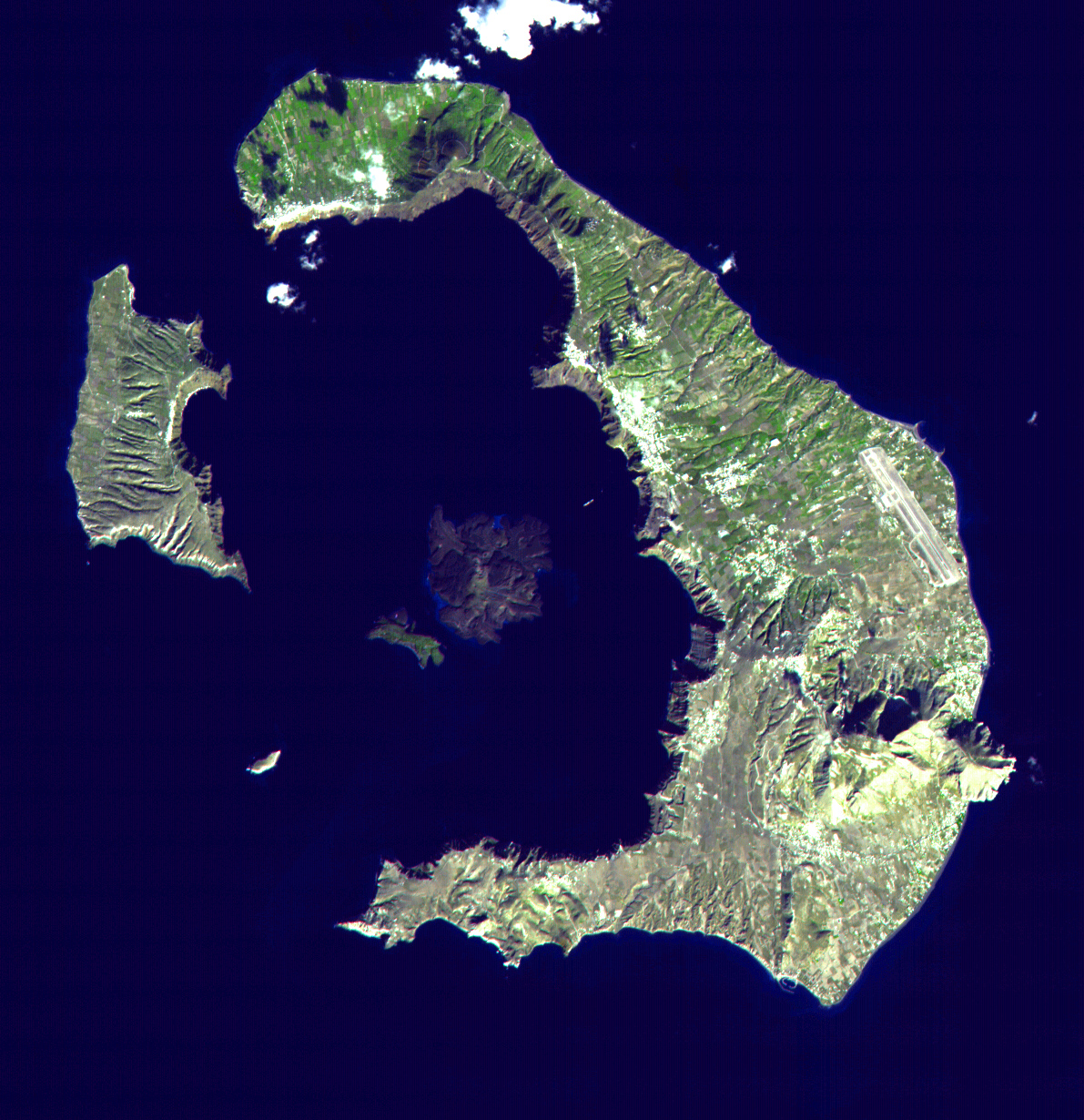
The Minoan eruption was a catastrophic volcanic eruption that devastated the Aegean island of Thera (also called Santorini) circa 1600 BC. It destroyed the Minoan settlement at Akrotiri, as well as communities and agricultural areas on nearby islands and the coast of Crete with subsequent earthquakes and tsunamis. With a Volcanic Explosivity Index (VEI) of 7, it resulted in the ejection of approximately 28–41 km3 (6.7–9.8 cu mi) of dense-rock equivalent (DRE), the eruption was one of the largest volcanic events in human history. Because tephra from the Minoan eruption serves as a marker horizon in nearly all archaeological sites in the Eastern Mediterranean, its precise date is of high importance and has been fiercely debated among archaeologists and volcanologists for decades, without coming to a definite conclusion. Although there are no clear ancient records of the eruption, its plume and volcanic lightning may have been described in the Egyptian Tempest Stele. The Chinese Bamboo Annals reported unusual yellow skies and summer frost at the beginning of the Shang dynasty, which may have been a consequence of volcanic winter (similar to 1816, the Year Without a Summer, after the 1815 eruption of Mount Tambora).
