Hurricane Gilbert
Updated: Wikipedia source
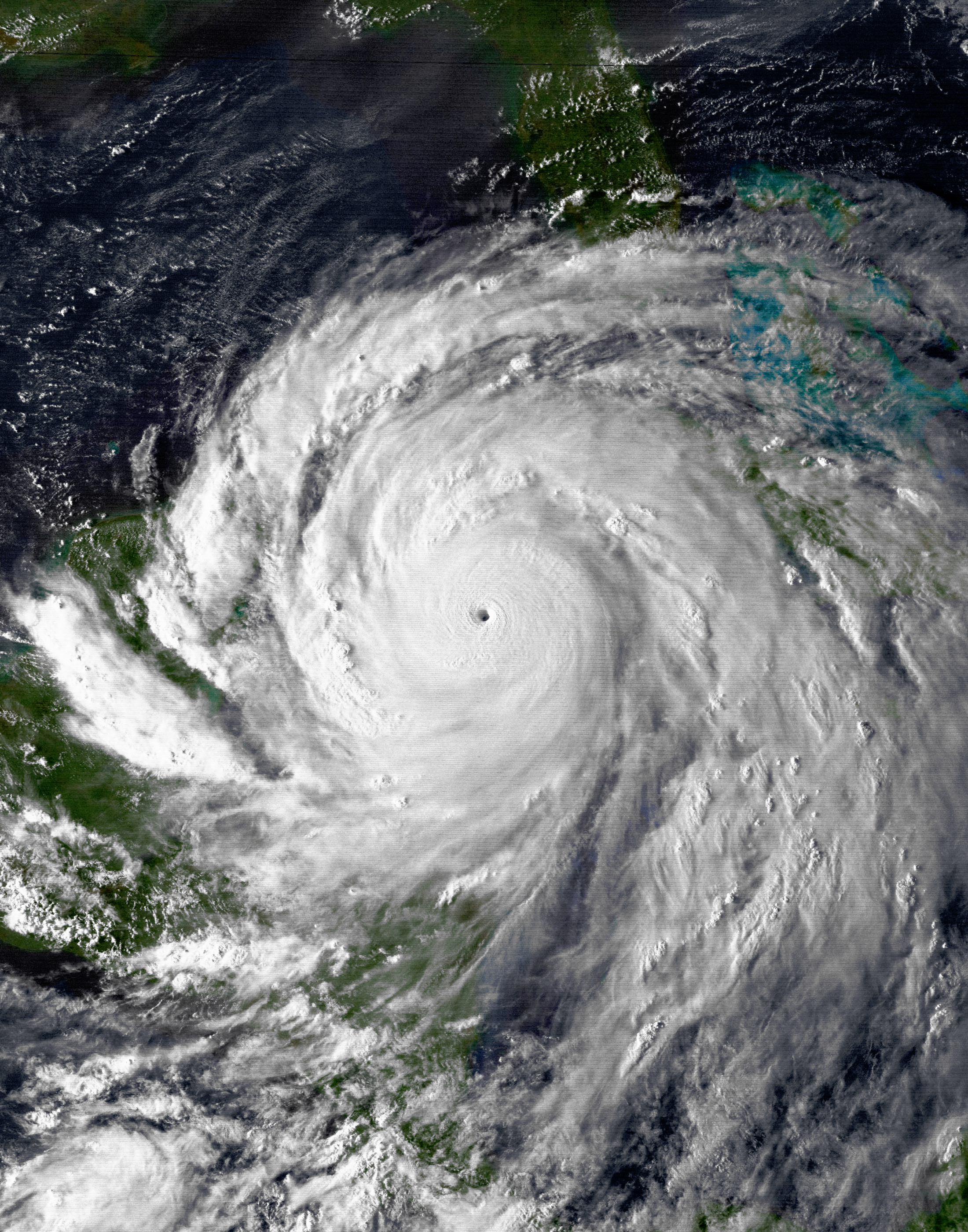
Hurricane Gilbert was a large and extremely powerful tropical cyclone that formed during the 1988 Atlantic hurricane season, which peaked as a Category 5 hurricane. The storm brought widespread destruction to the Caribbean and the Gulf of Mexico, and is tied with 1969's Hurricane Camille as the third-most intense tropical cyclone at landfall in the Atlantic Ocean. It was also the most intense tropical cyclone on record in the Atlantic basin in terms of barometric pressure, until it was surpassed by Hurricane Wilma in 2005. Gilbert was also one of the largest tropical cyclones ever observed in the Atlantic basin. At one point, its tropical storm-force winds measured 575 mi (925 km) in diameter. In addition, Gilbert was the most intense tropical cyclone in recorded history to strike Mexico. The seventh named storm, third hurricane and first major hurricane of the 1988 Atlantic hurricane season, Gilbert developed from a tropical wave on September 8 while located 400 mi (640 km) east of Barbados. Following intensification into a tropical storm the next day, Gilbert steadily strengthened as it tracked west-northwestward into the Caribbean Sea. On September 10, Gilbert attained hurricane intensity, and rapidly intensified into a Category 3 hurricane on September 11. After striking Jamaica the following day, rapid intensification occurred once again, and the storm became a Category 5 hurricane on the Saffir-Simpson scale with peak 1-minute sustained winds of 185 mph (298 km/h), late on September 13. Gilbert then weakened slightly, and made landfall on the Yucatán Peninsula later that day while maintaining Category 5 intensity. After landfall, Gilbert weakened rapidly over the Yucatán Peninsula, and emerged into the Gulf of Mexico as a Category 2 storm on September 15. Gradual intensification occurred as Gilbert tracked across the Gulf of Mexico, and the storm made landfall as a Category 3 hurricane in mainland Mexico on September 16. The hurricane gradually weakened after landfall, and eventually dissipated on September 19 over the Midwestern United States. Gilbert wrought havoc in the Caribbean and the Gulf of Mexico for nearly nine days. In total, it killed 318 people and caused about $2.98 billion (1988 USD) in damages along its path. As a result of the extensive damage caused by Gilbert, the World Meteorological Organization retired the name in the spring of 1989; it was replaced with Gordon for the 1994 hurricane season.
